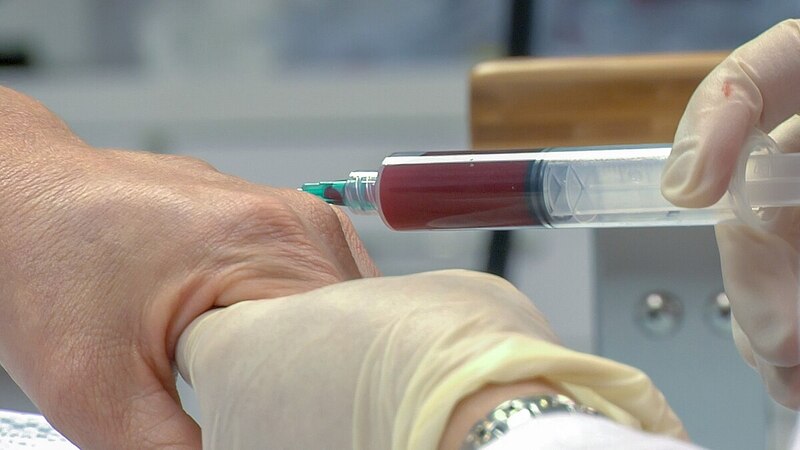
In recent years, Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy has gained increasing popularity as a novel and promising treatment option for a variety of medical conditions, ranging from orthopedic injuries to aesthetic concerns.
PRP therapy harnesses the body’s natural healing mechanisms by using concentrated platelets derived from the patient’s own blood to promote tissue repair and regeneration.
Understanding Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP)
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) is a biological product derived from the patient’s own blood, consisting of a concentrated mixture of platelets, growth factors, cytokines, and other bioactive molecules.
Platelets are small, disc-shaped blood cells that play a crucial role in the body’s natural healing process. When activated, platelets release a variety of growth factors and signaling molecules that stimulate tissue repair, promote angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels), and modulate inflammation.
The process of preparing PRP involves drawing a small sample of the patient’s blood and spinning it in a centrifuge machine to separate the platelets from other blood components, such as red blood cells and white blood cells. The resulting PRP solution is then collected and prepared for injection or application to the target tissue.
Mechanisms of Action
PRP therapy exerts its therapeutic effects through multiple mechanisms of action, including
1. Growth Factor Release
Platelets contain a multitude of growth factors, including platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and insulin-like growth factor (IGF), among others. These growth factors play key roles in stimulating cell proliferation, collagen synthesis, and tissue regeneration, thereby accelerating the healing process.
2. Angiogenesis
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and other angiogenic factors present in PRP promote the formation of new blood vessels, a process known as angiogenesis. Increased blood flow to the injured tissue enhances oxygen and nutrient delivery, facilitates waste removal, and promotes tissue repair and regeneration.
3. Anti-inflammatory Effects
PRP contains anti-inflammatory cytokines and factors that help modulate the inflammatory response, reducing pain, swelling, and tissue damage associated with injury or inflammation. By suppressing excessive inflammation, PRP therapy creates a more favorable environment for healing and tissue repair.
Clinical Applications of PRP Therapy
PRP therapy has shown promising results in a wide range of medical specialties, including orthopedics, sports medicine, dermatology, dentistry, and aesthetic medicine. Some common clinical applications of PRP therapy include:
1. Orthopedic Injuries
PRP therapy is commonly used in the treatment of musculoskeletal injuries, such as tendonitis, ligament sprains, muscle strains, and osteoarthritis. It has been particularly effective in conditions such as tennis elbow, golfer’s elbow, Achilles tendinopathy, rotator cuff tears, and knee osteoarthritis, where traditional treatments have been less successful.
2. Sports Medicine
Athletes and active individuals often experience acute and chronic injuries related to sports and physical activity. PRP therapy offers a non-surgical treatment option for speeding up the healing process and promoting tissue repair in conditions such as muscle tears, ligament injuries, and stress fractures.
3. Dental Procedures
PRP therapy is increasingly being used in oral and maxillofacial surgery to enhance tissue healing and promote bone regeneration following dental procedures such as tooth extractions, dental implant placement, and periodontal surgery. PRP can be applied topically or injected directly into the surgical site to accelerate soft tissue and bone healing.
4. Dermatology and Aesthetic Medicine
PRP therapy has gained popularity in dermatology and aesthetic medicine for its ability to rejuvenate the skin, stimulate hair growth, and improve overall skin quality. It is commonly used in procedures such as facial rejuvenation, acne scar treatment, hair restoration, and wound healing.
5. Chronic Wounds
Chronic wounds, such as diabetic ulcers, venous ulcers, and pressure ulcers, pose significant challenges in wound healing and management. PRP therapy has shown promise in promoting wound healing, reducing healing time, and improving outcomes in patients with chronic, non-healing wounds.
Potential Benefits of PRP Therapy
PRP therapy offers several potential benefits compared to traditional treatment modalities, including:
1. Safety
Since PRP is derived from the patient’s own blood, there is minimal risk of allergic reactions, infections, or other adverse effects. PRP therapy is considered a safe and well-tolerated treatment option for many patients.
2. Non-Surgical
PRP therapy is a minimally invasive, outpatient procedure that can be performed in the physician’s office or clinic setting. It offers a non-surgical alternative to traditional treatments such as corticosteroid injections, anti-inflammatory medications, and surgery.
3. Faster Recovery
PRP therapy promotes faster healing and tissue regeneration, allowing patients to return to normal activities more quickly than with conventional treatments. This is particularly beneficial for athletes and active individuals who wish to minimize downtime and resume their activities as soon as possible.
4. Long-lasting Results
PRP therapy can provide long-lasting relief from symptoms and improved functional outcomes, reducing the need for repeated treatments or interventions in many cases. The regenerative effects of PRP promote tissue repair and regeneration, leading to sustained improvements in pain, function, and quality of life.
5. Versatility
PRP therapy can be customized and tailored to meet the unique needs of each patient, making it a versatile treatment option for a wide range of medical conditions and injuries. It can be used alone or in conjunction with other treatments to enhance outcomes and optimize patient care.
Conclusion
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy represents a groundbreaking approach to healing and tissue regeneration, harnessing the body’s own natural healing mechanisms to promote recovery and improve outcomes in a variety of medical conditions.
With its ability to stimulate cell proliferation, enhance tissue repair, and modulate inflammation, PRP therapy offers a safe, effective, and minimally invasive treatment option for patients seeking relief from pain, dysfunction, and impaired healing.
As research continues to advance and our understanding of PRP therapy deepens, we can expect to see further innovations and refinements in its clinical applications, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and quality of life.